文章信息
标题
3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering
用于实时辐射场渲染的三维高斯投影方法
发表信息
文章发表于2023年的SIGGRAPH,并被评为2023年度的Best Paper.
论文链接
发表时间:[v1] Tue, 8 Aug 2023 06:37:06 UTC (33,218 KB)
文章内容
介绍
18-231206. 3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering. 论文发表于2023年的SIGGRAPH上,并被评为2023年SIGGRAPH的best paper. 文章将无界全范围场景下的新视角合成的速度和质量提上了一个很高的台阶,在训练三万轮(大约半个小时的训练时间)的时候,成像质量堪比或优于MipNeRF360;在训练7千轮(大约6-8分钟)的时候,成像质量也能够优于Instant-NGP。由于采用光栅化高斯球形投影方法,渲染速度能够达到一秒渲染93-135帧,此前最快的Instant-NGP的渲染速度是1秒渲染9帧,Plenoxels每秒8帧,MipNeRF大约十秒渲染一帧,实时渲染的性能相当可观。文章的方法主要由三点构成,第一使用各向异性的三维高斯作为场景的表示方法,在三维空间中朝向不同的高斯球,按照颜色、透明度,向成像平面加权投影,得到成像结果;第二是尺度适应性裁剪,高斯球的大小由协方差矩阵中的方差决定,方差越大表示高斯球的尺寸越大,可以用于表征空间中的大面积同质区域,文章适当地将大尺寸的高斯球分解为小尺寸的高斯球,逐步增强细节表征能力,最终的训练模型能达到场景中300-500k个小高斯球;第三是光栅化渲染算法,光栅化混合算法相比于NeRF的查询MLP更节省计算时间,最大程度提高渲染速度。
论文重点难点讲解
论文重点和难点
1 研究背景与动机
-
背景:神经辐射场(NeRF)技术在多视角图像合成领域取得了显著进展,但现有方法在训练和渲染速度上存在瓶颈,难以实现实时高质量渲染。
-
动机:本文提出一种基于3D高斯分布的场景表示方法,结合实时可微渲染器,旨在实现高质量的实时辐射场渲染,同时保持与现有最快方法相当的训练时间。
2 关键贡献
-
3D高斯分布表示:提出一种新颖的3D高斯分布场景表示方法,能够高效优化并支持快速渲染。该表示方法保留了连续体积辐射场的优化优势,同时避免了空空间的无效计算。
-
优化与密度控制:通过交错优化3D高斯分布的位置、各向异性协方差和透明度,并动态调整高斯分布的密度,实现了紧凑且精确的场景表示。
-
实时渲染算法:开发了一种基于瓦片的快速可见性感知渲染算法,支持各向异性高斯分布的“splatting”,加速训练并实现1080p分辨率下的实时渲染。
3 技术细节与难点
-
3D高斯分布的优化:
-
难点:高斯分布的协方差矩阵必须保持正半定性,而直接优化可能导致无效矩阵。为此,作者采用将协方差分解为缩放和旋转矩阵的方式进行优化,避免了这一问题。
-
公式:高斯分布的协方差矩阵$\Sigma$通过缩放矩阵$S$和旋转矩阵$R$表示为:
其中$S$为缩放矩阵,$R$为旋转矩阵。
-
各向异性高斯分布的渲染:
-
难点:如何高效地将3D高斯分布投影到2D屏幕空间,并进行快速排序和混合。
-
解决方案:通过瓦片化渲染和快速GPU排序算法,实现了各向异性高斯分布的实时渲染。渲染过程中,高斯分布按照深度排序并进行$\alpha$-blending,确保可见性顺序。
-
公式:高斯分布的2D投影公式为:
其中$J$是投影变换的雅可比矩阵。
-
实时渲染与训练效率:
-
难点:如何在保持高质量的同时,实现快速训练和实时渲染。
-
解决方案:通过交错优化和密度控制,以及高效的GPU实现,本文方法在训练速度上与现有最快方法相当,并在渲染速度上实现了显著提升。例如,在1080p分辨率下,本文方法能够达到135fps的实时渲染速度。
4 实验结果与对比
-
性能对比:
-
在多个标准数据集上,本文方法在训练时间、渲染速度和图像质量上均优于或接近现有最佳方法。例如,在Mip-NeRF360数据集上,本文方法在30K迭代后达到了25.2fps的渲染速度,而Mip-NeRF360的渲染速度仅为0.07fps。
-
定量结果:在PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS等指标上,本文方法与Mip-NeRF360相当或略优,同时训练时间大幅缩短。
-
实时性:本文方法首次实现了在1080p分辨率下高质量的实时辐射场渲染,填补了该领域的空白。
5 局限性与未来工作
-
局限性:
-
在未被充分观察的场景区域,本文方法可能会产生伪影。
-
各向异性高斯分布可能导致“拉伸”或“斑点”伪影。
-
内存消耗较高,尤其是在训练大规模场景时。
-
未来工作:
-
探索更高效的内存管理和优化策略。
-
将高斯分布表示应用于网格重建,以更好地理解其在体积表示和表面表示之间的位置。
-
改进可见性算法以减少伪影。
论文详细介绍
1 研究背景与动机
背景:
-
神经辐射场(NeRF)及其变体在多视角合成领域取得了显著成果,但现有方法在训练和渲染速度上存在瓶颈,难以实现实时高质量渲染。
-
现有方法分为两类:一类是高质量但训练和渲染速度慢(如Mip-NeRF360);另一类是训练和渲染速度快但质量较低(如InstantNGP和Plenoxels)。
动机:
- 提出一种新的方法,结合高质量和实时渲染的优点,实现1080p分辨率下的实时高质量多视角合成。
2 核心贡献
3D高斯分布表示:
-
使用3D高斯分布作为场景表示,结合各向异性协方差优化,实现紧凑且高效的场景建模。
-
从稀疏的Structure-from-Motion(SfM)点云初始化,避免了复杂的多视图立体(MVS)重建。
优化与密度控制:
- 通过交错优化3D高斯的位置、透明度、各向异性协方差和球谐系数,动态调整高斯分布的密度,避免过拟合和欠拟合。
实时渲染算法:
-
提出一种基于瓦片的快速可见性感知渲染算法,支持各向异性高斯分布的“splatting”,显著加速训练和渲染过程。
-
实现了1080p分辨率下的实时渲染(≥30fps),填补了该领域的空白。
3 技术细节
3D高斯分布的定义与优化:
定义:
-
每个3D高斯分布由位置(均值)$\mu$、各向异性协方差矩阵$\Sigma$、透明度$\alpha$和球谐系数(用于颜色表示)组成。
-
协方差矩阵$\Sigma$通过缩放矩阵$S$和旋转矩阵$R$表示为:
其中$S$为缩放矩阵,$R$为旋转矩阵。
优化:
-
使用梯度下降优化高斯分布的参数,通过球谐系数表示颜色,避免了神经网络的复杂性。
-
使用各向异性协方差优化,使高斯分布能够更好地适应复杂几何结构,减少参数数量。
密度控制与动态调整:
克隆(Clone)与分裂(Split)策略:
-
对于小尺度几何结构,通过克隆高斯分布来填补缺失区域。
-
对于大尺度高斯分布,通过分裂为多个小高斯分布来提高细节表现。
动态调整:
-
在优化过程中,动态添加或移除高斯分布,以适应场景的复杂性。
-
使用位置梯度的大小作为克隆或分裂的依据。
实时渲染算法:
瓦片化渲染:
-
将屏幕划分为16×16像素的瓦片,对每个瓦片内的高斯分布进行排序和渲染。
-
使用GPU的Radix排序算法对高斯分布进行深度排序,避免逐像素排序的开销。
各向异性“splatting”:
-
将3D高斯分布投影到2D屏幕空间,形成各向异性的椭圆分布。
-
通过$\alpha$-blending进行混合,确保可见性顺序。
反向传播:
- 在反向传播中,通过跟踪每个像素的累积透明度,支持任意数量的高斯分布接收梯度更新。
4 实验与结果
数据集与实验设置:
-
使用多个标准数据集(如Mip-NeRF360、Tanks&Temples、Deep Blending)进行测试。
-
在A6000 GPU上运行,与Mip-NeRF360、InstantNGP和Plenoxels等方法进行对比。
定量结果:
PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS:
-
在Mip-NeRF360数据集上,本文方法在30K迭代后达到了与Mip-NeRF360相当的PSNR和SSIM值,但训练时间从48小时缩短到35-45分钟。
-
在Tanks&Temples和Deep Blending数据集上,本文方法在PSNR和SSIM上优于InstantNGP和Plenoxels。
渲染速度:
- 本文方法在1080p分辨率下实现了135fps的实时渲染速度,而Mip-NeRF360仅为0.07fps。
定性结果:
-
本文方法在细节保留和背景重建方面优于Mip-NeRF360和InstantNGP。
-
在合成数据集(如Blender数据集)上,本文方法从随机初始化的高斯分布开始,也能快速收敛到高质量的结果。
5 局限性与未来工作
局限性:
-
在未被充分观察的区域,可能会出现伪影。
-
各向异性高斯分布可能导致“拉伸”或“斑点”伪影。
-
内存消耗较高,尤其是在训练大规模场景时。
未来工作:
-
探索更高效的内存管理和优化策略。
-
将高斯分布表示应用于网格重建,以更好地理解其在体积表示和表面表示之间的位置。
-
改进可见性算法以减少伪影。
6 总结
本文提出了一种基于3D高斯分布的实时辐射场渲染方法,通过高效的场景表示、优化策略和渲染算法,实现了高质量的实时渲染。该方法在训练时间、渲染速度和图像质量上均优于或接近现有最佳方法,为实时高质量多视角合成提供了一种新的解决方案。
论文方法部分详解
1 3D 高斯分布表示
本文提出了一种基于3D高斯分布的场景表示方法,用于高效优化和快速渲染。每个3D高斯分布由以下参数定义:
-
位置(均值):$\mu \in \mathbb{R}^3$
-
各向异性协方差矩阵:$\Sigma \in \mathbb{R}^{3 \times 3}$,用于表示高斯分布的形状和方向。
-
透明度:$\alpha \in [0, 1]$
-
球谐系数:用于表示颜色信息,支持视图依赖的外观。
关键点:
-
3D高斯分布是一种连续的体积表示,能够高效地表示复杂场景,同时避免了空空间的无效计算。
-
与传统的点云表示相比,3D高斯分布通过各向异性协方差矩阵能够更紧凑地表示几何细节。
2 从SfM点云初始化
输入为一组校准好的多视角图像及其对应的稀疏SfM点云。初始化步骤如下:
-
使用SfM点云作为初始的3D高斯分布中心(均值)。
-
初始协方差矩阵设置为各向同性,大小基于邻近点的距离。
-
初始透明度$\alpha$设置为较小值,以便在优化过程中逐渐调整。
公式:
初始协方差矩阵$\Sigma_0$为:
\[\Sigma_0 = \sigma_0^2 \mathbf{I}_3\]其中,$\sigma_0$是基于邻近点距离的标量,$\mathbf{I}_3$是3×3单位矩阵。
3 优化与密度控制
优化过程的目标是调整3D高斯分布的参数,以最小化渲染图像与训练视图之间的差异。优化步骤如下:
3.1 参数优化
-
使用随机梯度下降(SGD)优化3D高斯分布的位置、各向异性协方差、透明度和球谐系数。
-
透明度$\alpha$通过sigmoid激活函数约束在$[0, 1]$范围内。
-
协方差矩阵的优化通过分解为缩放矩阵$S$和旋转矩阵$R$实现:
- 优化过程中使用$L_1$损失和D-SSIM损失的组合:
其中,$\epsilon$为平衡参数。
3.2 密度控制
-
动态调整高斯分布的数量:通过克隆(Clone)和分裂(Split)策略动态调整高斯分布的密度。
-
克隆:对于小尺度高斯分布,通过复制并移动来填补缺失区域。
-
分裂:对于大尺度高斯分布,将其分裂为多个小高斯分布,以提高细节表现。
-
去除无效高斯分布:移除透明度小于阈值$\alpha_{\text{thresh}}$的高斯分布。
公式:
- 分裂策略中,新高斯分布的缩放因子为:
其中,$\pi_s$为实验确定的常数(如1.6)。
4 实时渲染算法
实时渲染是本文的核心贡献之一,通过以下技术实现高效渲染:
4.1 瓦片化渲染
-
将屏幕划分为16×16像素的瓦片,对每个瓦片内的高斯分布进行排序和渲染。
-
使用GPU的Radix排序算法对高斯分布按深度排序,避免逐像素排序的开销。
4.2 各向异性“splatting”
-
将3D高斯分布投影到2D屏幕空间,形成各向异性的椭圆分布。
-
使用$\alpha$-blending进行混合,确保可见性顺序。
公式:
高斯分布的2D投影协方差矩阵$\Sigma’$为:
\[\Sigma' = J \Sigma J^T\]其中,$J$是投影变换的雅可比矩阵。
4.3 反向传播
-
在反向传播中,通过跟踪每个像素的累积透明度,支持任意数量的高斯分布接收梯度更新。
-
通过存储每个像素的最终累积透明度,反向传播时能够恢复中间透明度值,从而计算梯度。
5 总结
本文提出的方法通过3D高斯分布的场景表示、动态优化与密度控制以及高效的实时渲染算法,实现了高质量的实时辐射场渲染。该方法在训练时间、渲染速度和图像质量上均优于或接近现有最佳方法,为实时高质量多视角合成提供了一种新的解决方案。
论文附录部分详解
附录A:梯度计算细节
附录A详细描述了3D高斯分布参数的梯度计算方法,这些梯度用于优化高斯分布的位置、各向异性协方差矩阵、透明度等参数。
- 位置梯度:
位置梯度的计算基于高斯分布的均值$\mu$对渲染结果的影响。位置梯度的表达式为:
\[\frac{\partial L}{\partial \mu} = -\sum_{i} \frac{\partial L}{\partial I_i} \cdot \frac{\partial I_i}{\partial \mu}\]其中,$L$是损失函数,$I_i$是像素$i$的渲染强度,$\frac{\partial I_i}{\partial \mu}$表示位置变化对像素强度的导数。
- 协方差矩阵梯度:
协方差矩阵$\Sigma$的梯度计算较为复杂,因为需要保持$\Sigma$的正定性。通过将$\Sigma$分解为缩放矩阵$S$和旋转矩阵$R$,可以更高效地计算梯度:
\[\Sigma = R S^2 R^T\]对应的梯度为:
\[\frac{\partial L}{\partial S} = 2 \cdot \frac{\partial L}{\partial \Sigma} \cdot S\] \[\frac{\partial L}{\partial R} = \frac{\partial L}{\partial \Sigma} \cdot S^2 \cdot R^T\]其中,$\frac{\partial L}{\partial \Sigma}$是损失函数对协方差矩阵的导数。
- 透明度梯度:
透明度$\alpha$的梯度计算较为直接,主要基于透明度对渲染结果的直接影响:
\[\frac{\partial L}{\partial \alpha} = -\sum_{i} \frac{\partial L}{\partial I_i} \cdot \frac{\partial I_i}{\partial \alpha}\]附录B:优化与密度控制算法
附录B提供了优化和密度控制算法的伪代码,详细描述了如何通过迭代优化高斯分布的参数,并动态调整高斯分布的数量。
- 算法流程:
1. 初始化:从SfM点云初始化高斯分布的位置、协方差、透明度和颜色。
2. 迭代优化:
-
采样训练视图并渲染当前高斯分布。
-
计算损失函数$L$并反向传播更新高斯分布参数。
-
每隔一定迭代次数,执行密度控制操作:
-
移除无效高斯分布:移除透明度小于阈值$\alpha_{\text{thresh}}$或尺寸过大的高斯分布。
-
克隆与分裂:根据位置梯度的大小,决定克隆小高斯分布或分裂大高斯分布。
3. 结束条件:当损失函数收敛或达到最大迭代次数时停止优化。
附录C:光栅化细节
附录C详细描述了基于瓦片的光栅化算法,用于高效渲染3D高斯分布。
-
瓦片化与排序:
-
将屏幕划分为16×16像素的瓦片。
-
对每个高斯分布计算其投影到屏幕空间的深度,并分配一个“键值”(key),其中低32位表示深度,高32位表示瓦片索引。
-
使用GPU的Radix排序算法对所有高斯分布进行全局排序。
-
渲染流程:
-
对每个瓦片,根据排序结果生成高斯分布列表。
-
按深度顺序对每个像素进行$\alpha$-blending混合,确保可见性顺序。
-
在反向传播中,通过存储每个像素的累积透明度,支持任意数量的高斯分布接收梯度更新。
-
数值稳定性:
-
在混合过程中,跳过透明度小于阈值(如$\frac{1}{255}$)的高斯分布,避免数值不稳定。
-
对透明度进行上界钳制(如0.99),防止累积透明度过高。
附录D:每场景误差指标
附录D提供了在不同数据集上,本文方法与其他方法(如Mip-NeRF360、InstantNGP、Plenoxels)的详细对比结果,包括PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS等指标。
-
数据集:
-
Mip-NeRF360数据集:包括多个复杂场景,如“bicycle”、“garden”、“room”等。
-
Tanks&Temples数据集:包含大规模室外场景。
-
Deep Blending数据集:包含室内场景。
-
对比结果:
-
本文方法在多个场景中达到了与Mip-NeRF360相当的PSNR和SSIM值,但在训练时间上大幅缩短(从48小时缩短到35-45分钟)。
-
在渲染速度上,本文方法实现了1080p分辨率下的实时渲染(≥30fps),而Mip-NeRF360仅为0.07fps。
-
在Tanks&Temples和Deep Blending数据集上,本文方法在PSNR和SSIM上优于InstantNGP和Plenoxels。
通过附录部分的详细描述,论文展示了其方法在优化、渲染和结果评估方面的具体实现细节,为读者提供了完整的实现参考。
部分关键问题讲解
3D Gaussian Splatting中的深度测试理解
Additionally, each pixel will only start (expensive) overlap testing and processing of points if their depth is lower than or equal to the depth of the last point that contributed to its color during the forward pass.
这句话描述的是3D Gaussian Splatting中的一种优化策略,用于减少计算量。让我来解释一下:
在3D Gaussian Splatting的渲染过程中,通常会有一个前向传递(forward pass),将3D高斯点投影到2D像素上。每个高斯点会影响多个像素,而每个像素也可能受到多个高斯点的影响。
这句话的意思是:
- 在前向传递中,每个像素会记录最后一个对其颜色有贡献的高斯点的深度值
- 在后续处理中(可能是反向传播或其他优化步骤),只有当新的高斯点的深度值小于或等于之前记录的深度值时,才会进行重叠测试和点处理
- 这是一种优化策略,因为深度测试是相对简单的操作,而重叠测试和点处理是计算密集型的(“expensive”)操作
这种策略本质上是一种基于深度的剔除(depth-based culling)技术,可以显著减少需要处理的点数量,从而提高渲染效率。它利用了一个事实:在大多数视角下,远处的点通常被近处的点遮挡,因此不需要对它们进行完整的处理。
这是3D Gaussian Splatting算法中的一种重要优化,使得实时渲染大规模点云成为可能。
原文翻译
3D高斯散射实现实时辐射场渲染
BERNHARD KERBL∗, Inria, 法国蔚蓝海岸大学
GEORGIOS KOPANAS∗, Inria, 法国蔚蓝海岸大学
THOMAS LEIMKÜHLER, 马克斯·普朗克信息学研究所, 德国
GEORGE DRETTAKIS, Inria, 法国蔚蓝海岸大学
辐射场方法最近彻底改变了使用多张照片或视频捕获的场景的新视角合成。然而,要实现高视觉质量仍然需要训练和渲染成本高昂的神经网络,而最近的更快方法不可避免地会以质量为代价换取速度。对于无界和完整的场景(而非孤立物体)和1080p分辨率渲染,目前没有方法能够达到实时显示速率。
我们引入三个关键元素,使我们能够实现最先进的视觉质量,同时保持有竞争力的训练时间,并且重要的是允许在1080p分辨率下进行高质量实时(≥ 30 fps)新视角合成。首先,从相机校准过程中产生的稀疏点开始,我们使用3D高斯表示场景,这保留了连续体积辐射场对场景优化的理想特性,同时避免了在空白空间中进行不必要的计算;其次,我们对3D高斯进行交错优化/密度控制,特别是优化各向异性协方差以实现对场景的准确表示;第三,我们开发了一种快速的可见性感知渲染算法,支持各向异性散射,既加速训练又允许实时渲染。我们在几个已建立的数据集上展示了最先进的视觉质量和实时渲染。
CCS概念:• 计算方法 → 渲染;基于点的模型;光栅化;机器学习方法。
附加关键词和短语:新视角合成,辐射场,3D高斯,实时渲染
ACM参考格式:
Bernhard Kerbl, Georgios Kopanas, Thomas Leimkühler, and George Drettakis. 2023. 3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering. ACM Trans. Graph. 42, 4, Article 1 (August 2023), 14 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3592433
1 引言
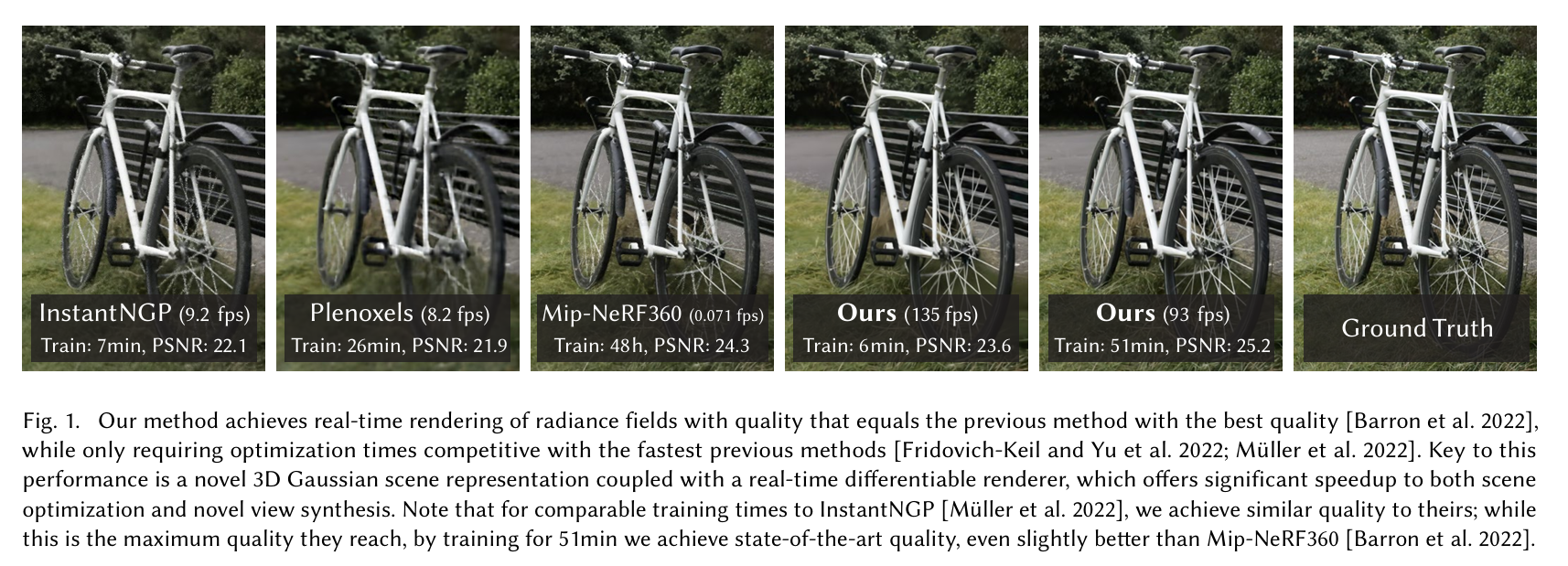
图1. 我们的方法实现了辐射场的实时渲染,其质量与之前质量最佳的方法[Barron等人,2022年]相当,同时所需的优化时间仅与之前最快的方法[Fridovich - Keil和Yu等人,2022年;Müller等人,2022年]具有竞争力。这种性能的关键在于一种新颖的三维高斯场景表示,结合了实时可微渲染器,这对场景优化和新视图合成都实现了显著的加速。请注意,与InstantNGP [Müller等人,2022年]相比,在相似的训练时间下,我们达到了与他们相似的质量;而这是他们能达到的最高质量,通过训练51分钟,我们达到了当前最优水平的质量,甚至比Mip - NeRF360 [Barron等人,2022年]略好。
网格和点是最常见的3D场景表示方法,因为它们是显式的,并且非常适合基于GPU/CUDA的快速光栅化。相比之下,最近的神经辐射场(NeRF)方法建立在连续场景表示之上,通常通过体积光线行进优化多层感知器(MLP),用于捕获场景的新视角合成。同样,迄今为止最高效的辐射场解决方案也建立在连续表示之上,通过插值存储在例如体素[Fridovich-Keil and Yu et al. 2022]或哈希[Müller et al. 2022]网格或点[Xu et al. 2022]中的值。虽然这些方法的连续性有助于优化,但渲染所需的随机采样成本高昂且可能产生噪声。我们引入了一种结合两者优点的新方法:我们的3D高斯表示允许以最先进(SOTA)的视觉质量和有竞争力的训练时间进行优化,而我们基于瓦片的散射解决方案确保在之前发布的多个数据集[Barron et al. 2022; Hedman et al. 2018; Knapitsch et al. 2017]上以SOTA质量进行1080p分辨率的实时渲染(见图1)。
我们的目标是允许对使用多张照片捕获的场景进行实时渲染,并以与之前最高效方法相当的优化时间为典型真实场景创建表示。最近的方法实现了快速训练[Fridovich-Keil and Yu et al. 2022; Müller et al. 2022],但难以达到当前SOTA NeRF方法(即Mip-NeRF360 [Barron et al. 2022])所获得的视觉质量,后者需要长达48小时的训练时间。这些快速但质量较低的辐射场方法可以根据场景实现交互式渲染时间(10-15帧每秒),但无法达到高分辨率的实时渲染。
我们的解决方案建立在三个主要组件上。首先,我们引入3D高斯作为灵活且富有表现力的场景表示。我们使用与之前类NeRF方法相同的输入,即通过结构光运动(SfM)[Snavely et al. 2006]校准的相机,并使用SfM过程中免费生成的稀疏点云初始化3D高斯集合。与大多数需要多视图立体(MVS)数据的基于点的解决方案[Aliev et al. 2020; Kopanas et al. 2021; Rückert et al. 2022]不同,我们仅使用SfM点作为输入就能实现高质量结果。值得注意的是,对于NeRF合成数据集,我们的方法即使使用随机初始化也能实现高质量。我们证明3D高斯是一个极佳的选择,因为它们是可微分的体积表示,但也可以通过将它们投影到2D并应用标准$\alpha$混合进行非常高效的光栅化,使用与NeRF等效的图像形成模型。我们方法的第二个组件是优化3D高斯的属性——3D位置、不透明度$\alpha$、各向异性协方差和球谐(SH)系数——与自适应密度控制步骤交错进行,在优化过程中添加并偶尔移除3D高斯。优化程序生成场景的合理紧凑、非结构化且精确的表示(所有测试场景为1-5百万高斯)。我们方法的第三个也是最后一个元素是我们的实时渲染解决方案,它使用快速GPU排序算法,并受到基于瓦片的光栅化的启发,遵循最近的工作[Lassner and Zollhofer 2021]。然而,由于我们的3D高斯表示,我们可以执行尊重可见性排序的各向异性散射——通过排序和$\alpha$混合——并通过跟踪所需的尽可能多的已排序散射点来实现快速准确的反向传播。
总结一下,我们提供以下贡献:
-
引入各向异性3D高斯作为辐射场的高质量、非结构化表示。
-
一种优化3D高斯属性的方法,与自适应密度控制交错进行,为捕获的场景创建高质量表示。
-
一种针对GPU的快速、可微分渲染方法,具有可见性感知,允许各向异性散射和快速反向传播,以实现高质量的新视角合成。
我们在之前发布的数据集上的结果表明,我们可以从多视图捕获中优化我们的3D高斯,并实现与最佳质量的先前隐式辐射场方法相当或更好的质量。我们还可以实现与最快方法相似的训练速度和质量,重要的是,我们提供了第一个具有高质量新视角合成的实时渲染解决方案。
2 相关工作
我们首先简要概述传统重建方法,然后讨论基于点的渲染和辐射场工作,探讨它们的相似性;辐射场是一个广泛的领域,因此我们仅关注直接相关的工作。有关该领域的完整覆盖,请参阅最近优秀的综述[Tewari et al. 2022; Xie et al. 2022]。
2.1 传统场景重建和渲染
最早的新视角合成方法基于光场,最初是密集采样[Gortler et al. 1996; Levoy and Hanrahan 1996],然后允许非结构化捕获[Buehler et al. 2001]。结构光运动(SfM)[Snavely et al. 2006]的出现开创了一个全新的领域,可以使用一系列照片合成新视角。SfM在相机校准过程中估计稀疏点云,最初用于3D空间的简单可视化。随后的多视图立体(MVS)多年来产生了令人印象深刻的完整3D重建算法[Goesele et al. 2007],促进了多种视图合成算法的发展[Chaurasia et al. 2013; Eisemann et al. 2008; Hedman et al. 2018; Kopanas et al. 2021]。所有这些方法将输入图像重新投影并混合到新视角相机中,并使用几何信息指导这种重投影。这些方法在许多情况下产生了出色的结果,但通常无法完全从未重建区域或”过度重建”(当MVS生成不存在的几何体时)中恢复。最近的神经渲染算法[Tewari et al. 2022]大大减少了此类伪影,并避免了在GPU上存储所有输入图像的巨大成本,在大多数方面优于这些方法。
2.2 神经渲染和辐射场
深度学习技术很早就被用于新视角合成[Flynn et al. 2016; Zhou et al. 2016];CNN被用来估计混合权重[Hedman et al. 2018],或用于纹理空间解决方案[Riegler and Koltun 2020; Thies et al. 2019]。使用基于MVS的几何是这些方法的主要缺点;此外,使用CNN进行最终渲染经常导致时间闪烁。
体积表示用于新视角合成始于Soft3D[Penner and Zhang 2017];随后提出了与体积光线行进相结合的深度学习技术[Henzler et al. 2019; Sitzmann et al. 2019],建立在连续可微密度场上以表示几何。使用体积光线行进进行渲染由于查询体积所需的大量样本而成本显著。神经辐射场(NeRF)[Mildenhall et al. 2020]引入了重要性采样和位置编码来提高质量,但使用了大型多层感知器,对速度产生负面影响。NeRF的成功导致了大量后续方法的涌现,这些方法解决了质量和速度问题,通常通过引入正则化策略;当前新视角合成的图像质量最先进的是Mip-NeRF360[Barron et al. 2022]。虽然渲染质量出色,但训练和渲染时间仍然极高;我们能够达到或在某些情况下超越这种质量,同时提供快速训练和实时渲染。
最近的方法主要通过利用三种设计选择来关注更快的训练和/或渲染:使用空间数据结构存储在体积光线行进期间随后插值的(神经)特征,不同的编码,以及MLP容量。这些方法包括空间离散化的不同变体[Chen et al. 2022b,a; Fridovich-Keil and Yu et al. 2022; Garbin et al. 2021; Hedman et al. 2021; Reiser et al. 2021; Takikawa et al. 2021; Wu et al. 2022; Yu et al. 2021],码本[Takikawa et al. 2022],以及哈希表等编码[Müller et al. 2022],允许使用更小的MLP或完全放弃神经网络[Fridovich-Keil and Yu et al. 2022; Sun et al. 2022]。
这些方法中最值得注意的是InstantNGP [Müller等人 2022],它使用哈希网格和占用网格来加速计算,并使用较小的多层感知器(MLP)来表示密度和外观;还有Plenoxels [Fridovich - Keil和Yu等人 2022],它使用稀疏体素网格来插值连续的密度场,并且完全无需神经网络。这两种方法都依赖球谐函数:前者直接表示方向效应,后者将其输入编码到颜色网络中。虽然这两种方法都能提供出色的结果,但这些方法在有效表示空白空间方面仍可能存在困难,这在一定程度上取决于场景/捕获类型。此外,图像质量在很大程度上受到用于加速的结构化网格选择的限制,并且由于在给定的光线行进步骤中需要查询许多样本,渲染速度也受到阻碍。我们使用的无结构、显式且对GPU友好的三维高斯模型,在没有神经组件的情况下实现了更快的渲染速度和更高的质量。
2.3 基于点的渲染和辐射场
基于点的方法可以高效地渲染不连续且无结构的几何样本(即点云)[Gross和Pfister 2011]。最简单形式的点样本渲染[Grossman和Dally 1998] 对一组固定大小的无结构点进行光栅化,它可以利用图形API原生支持的点类型[Sainz和Pajarola 2004],或者在GPU上进行并行软件光栅化[Laine和Karras 2011; Schütz等人 2022]。虽然点样本渲染忠实于底层数据,但它存在孔洞问题,会导致混叠,并且是严格不连续的。关于高质量基于点的渲染的开创性工作通过“喷绘”(splatting) 范围大于一个像素的点基元来解决这些问题,例如圆形或椭圆形圆盘、椭球体或曲面元素[Botsch等人 2005; Pfister等人 2000; Ren等人 2002; Zwicker等人 2001b]。
最近,人们对可微的基于点的渲染技术产生了兴趣[Wiles等人 2020; Yifan等人 2019]。点被赋予了神经特征,并使用卷积神经网络(CNN)进行渲染[Aliev等人 2020; Rückert等人 2022],从而实现快速甚至实时的视图合成;然而,它们仍然依赖多视图立体(MVS)来获取初始几何结构,因此也继承了其缺陷,在诸如无特征/有光泽区域或薄结构等复杂情况下,最明显的是过度或欠重建问题。
基于点的α混合和神经辐射场(NeRF)风格的体渲染本质上共享相同的成像模型。具体来说,颜色$C$由沿光线的体渲染给出:
\[C = \sum_{i = 1}^{N} T_{i}(1 - \exp(-\sigma_{i}\delta_{i}))\mathbf{c}_{i} \text{ ,其中 } T_{i} = \exp\left(- \sum_{j = 1}^{i - 1} \sigma_{j}\delta_{j}\right), \quad (1)\]其中,密度$\sigma$、透射率$T$和颜色$\mathbf{c}$的样本是沿着光线以间隔$\delta_{i}$获取的。这可以改写为
\[C = \sum_{i = 1}^{N} T_{i}\alpha_{i}\mathbf{c}_{i}, \tag{2}\]其中
\[\alpha_{i} = (1 - \exp(-\sigma_{i}\delta_{i})) \text{ 且 } T_{i} = \prod_{j = 1}^{i - 1}(1 - \alpha_{i})\]一种典型的基于神经点的方法(例如,[Kopanas等人 2022, 2021])通过混合与像素重叠的$N$个有序点来计算像素的颜色$C$:
\[C = \sum_{i \in \mathcal{N}} c_{i}\alpha_{i} \prod_{j = 1}^{i - 1}(1 - \alpha_{j}), \tag{3}\]其中$\mathbf{c}{i}$是每个点的颜色,$\alpha{i}$通过计算协方差为$\Sigma$的二维高斯函数[Yifan等人 2019] 并乘以每个点学习到的不透明度来得到。
从等式2和等式3中,我们可以清楚地看到图像形成模型是相同的。然而,渲染算法非常不同。NeRF是一种连续表示,隐式地表示空/占用空间;需要昂贵的随机采样来找到等式2中的样本,导致噪声和计算成本。相比之下,点是一种非结构化、离散的表示,足够灵活,允许创建、销毁和移动几何体,类似于NeRF。这是通过优化不透明度和位置实现的,如先前工作[Kopanas et al. 2021]所示,同时避免了完全体积表示的缺点。
Pulsar[Lassner and Zollhofer 2021]实现了快速球体光栅化,这启发了我们基于瓦片和排序的渲染器。然而,根据上述分析,我们希望在排序后的散射点上保持(近似)传统的$\alpha$混合,以获得体积表示的优势:我们的光栅化尊重可见性顺序,与他们的顺序无关方法相反。此外,我们对像素中的所有散射点反向传播梯度,并光栅化各向异性散射点。这些元素都有助于我们结果的高视觉质量(见第7.3节)。此外,上述先前方法还使用CNN进行渲染,导致时间不稳定性。尽管如此,Pulsar[Lassner and Zollhofer 2021]和ADOP[Rückert et al. 2022]的渲染速度激励我们开发了快速渲染解决方案。
虽然专注于镜面效果,Neural Point Catacaustics[Kopanas et al. 2022]的漫反射基于点的渲染通过使用MLP克服了这种时间不稳定性,但仍然需要MVS几何作为输入。该类别中最新的方法[Zhang et al. 2022]不需要MVS,也使用SH表示方向;然而,它只能处理一个物体的场景,并且需要掩码进行初始化。虽然对于小分辨率和低点数量来说很快,但不清楚它如何扩展到典型数据集[Barron et al. 2022; Hedman et al. 2018; Knapitsch et al. 2017]的场景。我们使用3D高斯作为更灵活的场景表示,避免了对MVS几何的需求,并且由于我们针对投影高斯的基于瓦片的渲染算法而实现了实时渲染。
最近的一种方法[Xu et al. 2022]使用点通过径向基函数方法表示辐射场。他们在优化过程中采用点修剪和密集化技术,但使用体积光线行进,无法实现实时显示速率。
在人体表演捕捉领域,3D高斯已被用于表示捕获的人体[Rhodin et al. 2015; Stoll et al. 2011];最近,它们已与体积光线行进一起用于视觉任务[Wang et al. 2023]。神经体积基元已在类似上下文中被提出[Lombardi et al. 2021]。虽然这些方法启发了我们选择3D高斯作为场景表示,但它们专注于重建和渲染单个孤立物体(人体或面部)的特定情况,导致深度复杂性较小的场景。相比之下,我们对各向异性协方差的优化、交错优化/密度控制以及用于渲染的高效深度排序使我们能够处理包括背景在内的完整复杂场景,无论是室内还是室外,且具有大的深度复杂性。
3 概述
我们方法的输入是一组静态场景的图像,以及通过SfM[Schönberger and Frahm 2016]校准的相应相机,该过程副产品是一个稀疏点云。从这些点我们创建一组3D高斯(第4节),由位置(均值)、协方差矩阵和不透明度$\alpha$定义,允许非常灵活的优化机制。这产生了3D场景的合理紧凑表示,部分原因是高度各向异性的体积散射点可用于紧凑地表示精细结构。辐射场的方向外观组件(颜色)通过球谐函数(SH)表示,遵循标准做法[Fridovich-Keil and Yu et al. 2022; Müller et al. 2022]。我们的算法通过一系列3D高斯参数的优化步骤来创建辐射场表示(第5节),即位置、协方差、$\alpha$和SH系数,与高斯密度自适应控制操作交错进行。
我们方法效率的关键是我们基于瓦片的光栅化器(第6节),它允许各向异性散射点的$\alpha$混合,由于快速排序而尊重可见性顺序。我们的快速光栅化器还包括通过跟踪累积$\alpha$值的快速反向传递,对可接收梯度的高斯数量没有限制。我们方法的概述如图2所示。
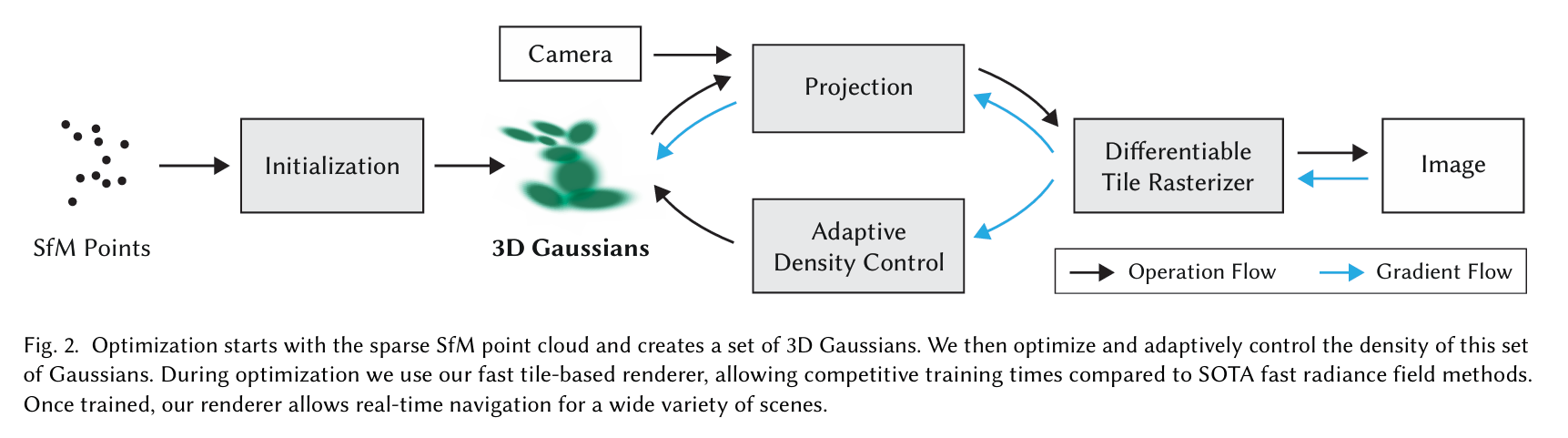
图2. 优化从稀疏的运动结构(SfM)点云开始,并创建一组三维高斯。然后我们对这组高斯进行优化并自适应地控制其密度。在优化过程中,我们使用快速的基于图块的渲染器,与当前最优的快速辐射场方法相比,实现了具有竞争力的训练时间。一旦训练完成,我们的渲染器能够对各种场景进行实时导航。
4 可微分3D高斯散射
我们的目标是优化一种场景表示,允许高质量的新视角合成,从一组没有法线的稀疏(SfM)点开始。为此,我们需要一种原语,它继承可微分体积表示的特性,同时又是非结构化和显式的,以允许非常快速的渲染。我们选择3D高斯,它们是可微分的,可以轻松投影到2D散射点,允许快速$\alpha$混合进行渲染。
我们的表示方法与先前使用二维点的方法[Kopanas等人 2021; Yifan等人 2019]有相似之处,这些方法假设每个点是一个带有法向量的小平面圆。鉴于从运动恢复结构(SfM)点的极度稀疏性,估计法向量非常困难。同样,从这样的估计中优化噪声很大的法向量也极具挑战性。相反,我们将几何形状建模为一组不需要法向量的三维高斯模型。我们的高斯模型由在世界空间中定义的完整三维协方差矩阵$\Sigma$确定[Zwicker等人 2001a],其中心位于点(均值)$\mu$处:
\[G(x) = e^{-\frac{1}{2}(x)^{T}\Sigma^{-1}(x)} \tag{4}\]在我们的混合过程中,这个高斯模型要乘以$\alpha$。
然而,为了进行渲染,我们需要将三维高斯模型投影到二维。Zwicker等人[2001a]展示了如何将其投影到图像空间。给定一个视图变换$W$,相机坐标系中的协方差矩阵$\Sigma’$如下所示:
\[\Sigma' = JW\Sigma W^{T}J^{T} \tag{5}\]其中$J$是投影变换的仿射近似的雅可比矩阵。Zwicker等人[2001a]还表明,如果我们跳过$\Sigma’$的第三行和第三列,我们会得到一个$2\times2$的方差矩阵,其结构和属性与我们从带有法向量的平面点开始(如先前工作[Kopanas等人 2021]中那样)得到的相同。
一个显而易见的方法是直接优化协方差矩阵$\Sigma$,以获得表示辐射场的三维高斯模型。然而,协方差矩阵只有在半正定的情况下才有物理意义。对于我们对所有参数的优化,我们使用梯度下降法,但这种方法不容易被约束以生成这样的有效矩阵,并且更新步骤和梯度很容易产生无效的协方差矩阵。
因此,我们选择了一种更直观但表达能力等效的表示方法用于优化。三维高斯模型的协方差矩阵$\Sigma$类似于描述一个椭球体的构型。给定一个缩放矩阵$S$和旋转矩阵$R$,我们可以找到对应的$\Sigma$:
\[\Sigma = RSS^{T}R^{T} \tag{6}\]为了能够独立优化这两个因素,我们将它们分开存储:一个用于缩放的三维向量$s$和一个表示旋转的四元数$q$。这些可以很容易地转换为它们各自的矩阵并组合起来,同时要确保对$q$进行归一化以获得有效的单位四元数。
为了避免在训练期间由于自动求导带来的显著开销,我们显式地推导所有参数的梯度。精确导数计算的详细信息见附录A。
这种各向异性协方差的表示方法——适合优化——使我们能够优化三维高斯模型,以适应捕获场景中不同形状的几何结构,从而得到一种相当紧凑的表示。图3展示了这样的情况。
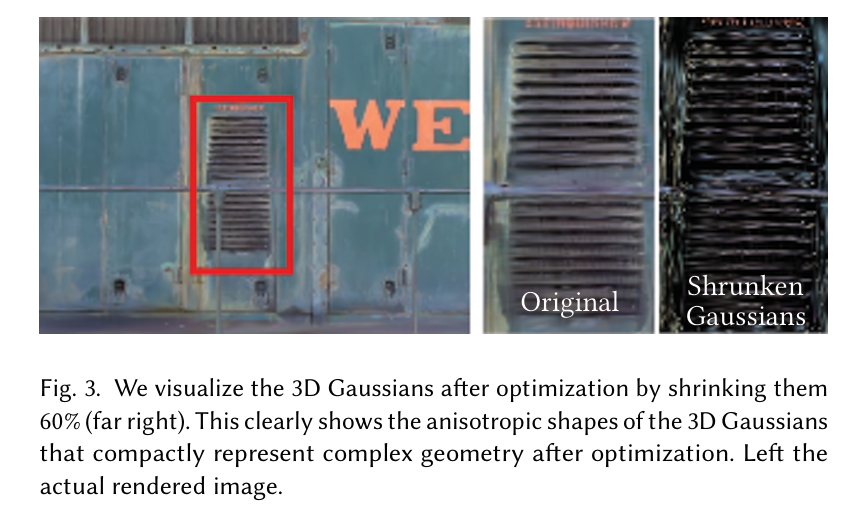
图3. 我们通过将优化后的三维高斯缩小60%(最右侧)来进行可视化。这清楚地展示了三维高斯的各向异性形状,在优化后紧凑地表示了复杂的几何结构。左侧是实际渲染的图像。
5 具有自适应密度的三维高斯模型优化控制
我们方法的核心是优化步骤,该步骤创建一组密集的三维高斯模型,以准确表示场景,用于自由视角合成。除了位置$p$、$\alpha$和协方差$\Sigma$之外,我们还优化表示每个高斯模型颜色$c$的球谐函数(SH)系数,以正确捕捉场景中与视角相关的外观。这些参数的优化与控制高斯模型密度的步骤相互交织,以便更好地表示场景。
5.1 优化
优化基于渲染的连续迭代,并将生成的图像与捕获数据集中的训练视图进行比较。由于从三维到二维投影的模糊性,几何形状可能会被错误放置。因此,我们的优化需要能够创建几何形状,并且如果几何形状放置错误,还能够消除或移动它。三维高斯模型协方差参数的质量对于表示的紧凑性至关重要,因为大的均匀区域可以用少量大的各向异性高斯模型来捕获。
我们使用随机梯度下降技术进行优化,充分利用标准的GPU加速框架,并且能够像近期的最佳实践那样[Fridovich - Keil和Yu等人 2022; Sun等人 2022],为某些操作添加自定义CUDA内核。特别是,我们的快速光栅化(见第6节)对优化效率至关重要,因为它是优化过程中的主要计算瓶颈。
我们对$\alpha$使用sigmoid激活函数,将其限制在$[0 - 1)$范围内并获得平滑的梯度,出于类似的原因,对协方差的尺度使用指数激活函数。
我们将初始协方差矩阵估计为各向同性高斯模型,其轴长等于到最近三个点距离的平均值。我们使用类似于Plenoxels [Fridovich - Keil和Yu等人 2022]的标准指数衰减调度技术,但仅用于位置。损失函数是$L_1$与D - SSIM项的组合:
\[\mathcal{L} = (1 - \lambda)\mathcal{L}_1 + \lambda\mathcal{L}_{\text{D-SSIM}} \tag{7}\]在所有测试中我们都使用$\lambda = 0.2$。我们在7.1节中提供学习调度和其他要素的详细信息。
5.2 高斯的自适应控制
我们从SfM的初始稀疏点集开始,然后应用我们的方法自适应地控制高斯的数量和它们在单位体积上的密度¹,使我们能够从初始稀疏高斯集合转变为更密集的集合,更好地表示场景,并具有正确的参数。在优化预热后(见第7.1节),我们每100次迭代进行密集化,并移除任何基本透明的高斯,即$\alpha$小于阈值$\varepsilon_\alpha$的高斯。
我们对高斯的自适应控制需要填充空白区域。它专注于缺少几何特征的区域(”欠重建”),也关注高斯覆盖场景大面积的区域(通常对应于”过度重建”)。我们观察到两者都有较大的视图空间位置梯度。直观地说,这可能是因为它们对应于尚未很好重建的区域,优化试图移动高斯来纠正这一点。
由于这两种情况都是密集化的良好候选,我们对视图空间位置梯度平均幅度超过阈值$\tau_{pos}$的高斯进行密集化,在我们的测试中设置为0.0002。接下来我们介绍这个过程的细节,如图4所示。
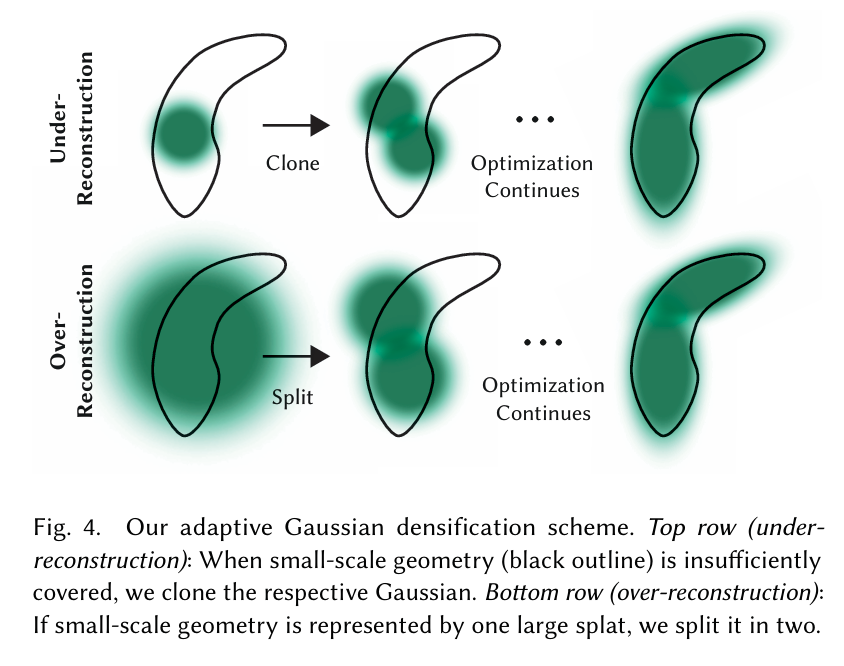
图4. 我们的自适应高斯密度化方案。上排(重建不足):当小尺度几何结构(黑色轮廓)覆盖不足时,我们复制相应的高斯。下排(过度重建):如果小尺度几何结构由一个大的喷溅表示,我们将其分成两个。
对于处于欠重建区域的小高斯,我们需要覆盖必须创建的新几何体。为此,最好克隆高斯,只需创建相同大小的副本,并将其沿位置梯度方向移动。另一方面,高方差区域中的大高斯需要分裂成更小的高斯。我们用两个新高斯替换这样的高斯,并将它们的尺度除以因子$\phi = 1.6$,这是我们通过实验确定的。我们还通过使用原始3D高斯作为PDF进行采样来初始化它们的位置。
在第一种情况下,我们检测并处理增加系统总体积和高斯数量的需求,而在第二种情况下,我们保持总体积不变但增加高斯数量。与其他体积表示类似,我们的优化可能会在输入相机附近出现浮动物;在我们的情况下,这可能导致高斯密度不合理地增加。控制高斯数量增加的有效方法是每$N = 3000$次迭代将$\alpha$值设置为接近零。然后优化会在需要的地方增加高斯的$\alpha$,同时允许我们的剔除方法移除$\alpha$小于$\varepsilon_\alpha$的高斯,如上所述。高斯可能会收缩或增长并与其他高斯显著重叠,但我们定期移除在世界空间中非常大的高斯和在视图空间中有大足迹的高斯。这种策略对高斯总数提供了总体良好的控制。我们模型中的高斯始终保持为欧几里得空间中的基元;与其他方法[Barron et al. 2022; Fridovich-Keil and Yu et al. 2022]不同,我们不需要对远距离或大型高斯进行空间压缩、扭曲或投影策略。
6 高斯快速可微分光栅化器
我们的目标是实现快速的整体渲染和快速排序,以允许近似$\alpha$混合——包括各向异性散射点——并避免先前工作[Lassner and Zollhofer 2021]中存在的对可接收梯度的散射点数量的硬性限制。
为实现这些目标,我们设计了一个基于瓦片的高斯散射点光栅化器,受最近软件光栅化方法[Lassner and Zollhofer 2021]的启发,一次性对整个图像的基元进行预排序,避免了之前$\alpha$混合解决方案[Kopanas et al. 2022, 2021]中每像素排序的开销。我们的快速光栅化器允许对任意数量的混合高斯进行高效反向传播,只需要每像素恒定的额外内存消耗。我们的光栅化管线完全可微分,并且考虑到投影到2D(第4节),可以像之前的2D散射方法[Kopanas et al. 2021]一样光栅化各向异性散射点。
我们的方法首先将屏幕分割为16×16的瓦片,然后对3D高斯进行视锥体和每个瓦片的剔除。具体来说,我们只保留99%置信区间与视锥体相交的高斯。此外,我们使用保护带来简单拒绝处于极端位置的高斯(即那些均值接近近平面且远离视锥体的高斯),因为计算它们的投影2D协方差将不稳定。然后,我们根据高斯与重叠瓦片的数量实例化每个高斯,并为每个实例分配一个结合视图空间深度和瓦片ID的键。然后,我们使用单个快速GPU基数排序[Merrill and Grimshaw 2010]基于这些键对高斯进行排序。请注意,没有额外的每像素点排序,混合是基于这个初始排序执行的。因此,在某些配置中,我们的$\alpha$混合可能是近似的。然而,随着散射点接近单个像素的大小,这些近似变得可以忽略。我们发现这种选择大大提高了训练和渲染性能,而不会在收敛场景中产生可见伪影。
排序高斯后,我们通过识别散射到给定瓦片的第一个和最后一个按深度排序的条目,为每个瓦片生成一个列表。对于光栅化,我们为每个瓦片启动一个线程块。每个块首先协作地将高斯数据包加载到共享内存中,然后对于给定像素,通过从前到后遍历列表来累积颜色和$\alpha$值,从而最大化数据加载/共享和处理的并行性增益。当我们在像素中达到目标$\alpha$饱和度时,相应的线程停止。在定期间隔,查询瓦片中的线程,当所有像素都饱和时(即$\alpha$达到1),整个瓦片的处理终止。排序的详细信息和整体光栅化方法的高级概述在附录C中给出。
在光栅化过程中,$\alpha$的饱和是唯一的停止标准。与之前的工作相比,我们不限制接收梯度更新的混合基元的数量。我们强制执行这一特性,使我们的方法能够处理具有任意、变化深度复杂性的场景并准确学习它们,而无需求助于特定场景的超参数调整。因此,在反向传递过程中,我们必须恢复前向传递中每像素混合点的完整序列。一种解决方案是在全局内存中存储每像素任意长的混合点列表[Kopanas et al. 2021]。为避免隐含的动态内存管理开销,我们选择再次遍历每瓦片列表;我们可以重用前向传递中的已排序高斯数组和瓦片范围。为便于梯度计算,我们现在从后向前遍历它们。
遍历从影响瓦片中任何像素的最后一个点开始,点的共享内存加载再次协作进行。此外,每个像素只有在点的深度小于或等于前向传递中对其颜色有贡献的最后一个点的深度时,才会开始(昂贵的)重叠测试和点处理。计算第4节中描述的梯度需要原始混合过程中每一步的累积不透明度值。我们不需要在反向传递中遍历逐渐缩小的不透明度的显式列表,而是可以通过仅存储前向传递结束时的总累积不透明度来恢复这些中间不透明度。具体来说,每个点存储前向过程中的最终累积不透明度$\alpha$;在我们的从后到前遍历中,我们将其除以每个点的$\alpha$,以获得梯度计算所需的系数。
7 实现、结果和评估
接下来我们讨论一些实现细节,展示结果并评估我们的算法与先前工作的比较以及消融研究。
7.1 实现
我们使用PyTorch框架在Python中实现了我们的方法,并编写了用于光栅化的自定义CUDA内核,这些内核是先前方法[Kopanas et al. 2021]的扩展版本,并使用NVIDIA CUB排序例程进行快速基数排序[Merrill and Grimshaw 2010]。我们还使用开源SIBR[Bonopera et al. 2020]构建了一个交互式查看器,用于交互式查看。我们使用此实现来测量我们实现的帧率。源代码和所有数据可在以下网址获取:
https://repo-sam.inria.fr/fungraph/3d-gaussian-splatting/
优化细节。为了稳定性,我们在较低分辨率下”预热”计算。具体来说,我们使用4倍小的图像分辨率开始优化,并在250和500次迭代后进行两次上采样。
SH系数优化对角度信息的缺乏很敏感。对于典型的”类NeRF”捕获,其中中心物体由在其周围整个半球拍摄的照片观察,优化效果良好。然而,如果捕获有角度区域缺失(例如,当捕获场景的角落,或执行”由内向外”[Hedman et al. 2016]捕获)时,优化可能会产生完全不正确的SH零阶分量(即基础或漫反射颜色)值。为了克服这个问题,我们首先只优化零阶分量,然后在每1000次迭代后引入一个SH波段,直到所有4个SH波段都被表示。
7.2 结果和评估
结果。我们在来自先前发布的数据集的总共13个真实场景和合成Blender数据集[Mildenhall et al. 2020]上测试了我们的算法。特别是,我们在Mip-Nerf360[Barron et al. 2022](当前NeRF渲染质量的最先进水平)中呈现的全套场景、Tanks&Temples数据集[2017]中的两个场景以及Hedman等人[Hedman et al. 2018]提供的两个场景上测试了我们的方法。我们选择的场景具有非常不同的捕获风格,涵盖了有界室内场景和大型无界户外环境。我们在评估中的所有实验中使用相同的超参数配置。所有结果都是在A6000 GPU上运行的,除了Mip-NeRF360方法(见下文)。
在补充材料中,我们展示了一系列场景的渲染视频路径,这些场景包含远离输入照片的视图。
真实世界场景。在质量方面,当前最先进的是Mip-Nerf360[Barron et al. 2021]。我们将其作为质量基准进行比较。我们还与两种最新的快速NeRF方法进行比较:InstantNGP[Müller et al. 2022]和Plenoxels[Fridovich-Keil and Yu et al. 2022]。
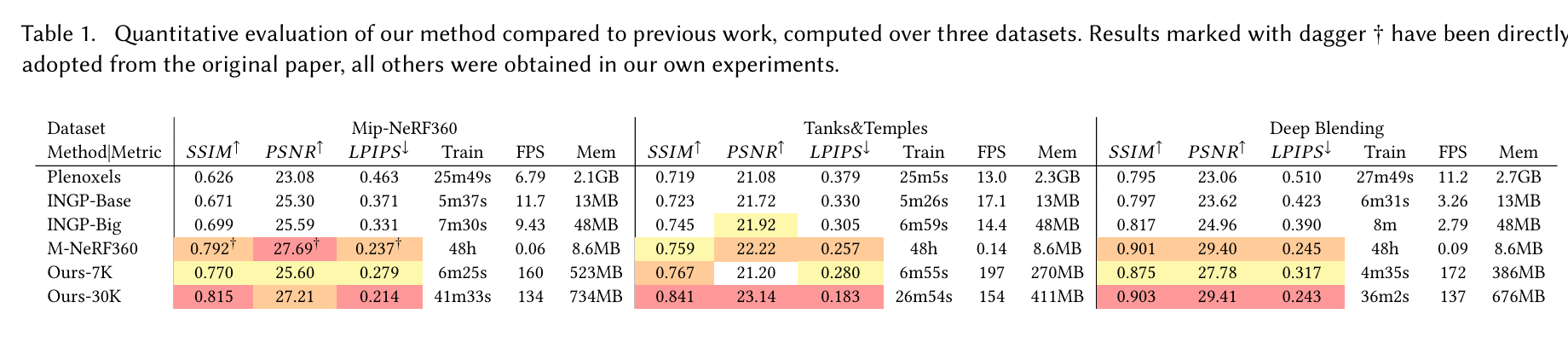
表 1. 我们的方法与先前工作的定量评估,在三个数据集上计算得出。标记有剑号†的结果直接取自原文,其他所有结果均来自我们自己的实验。
我们对数据集使用训练/测试分割,采用Mip-NeRF360建议的方法,每8张照片取一张作为测试,以便进行一致且有意义的比较,生成错误指标,使用文献中最常用的标准PSNR、L-PIPS和SSIM指标;请参见表1。表中的所有数字都来自我们自己运行所有先前方法的作者代码,除了Mip-NeRF360在其数据集上的数字,我们从原始出版物中复制了这些数字,以避免对当前SOTA的混淆。对于我们图中的图像,我们使用了我们自己运行的Mip-NeRF360:这些运行的数字在附录D中。我们还显示了平均训练时间、渲染速度和用于存储优化参数的内存。我们报告了InstantNGP的基本配置(Base)运行35K次迭代的结果,以及作者建议的稍大网络(Big),以及我们的两种配置,7K和30K次迭代。我们在图6中展示了我们两种配置的视觉质量差异。在许多情况下,7K次迭代的质量已经相当好。

图6. 对于某些场景(上图),我们可以看到,即使在7000次迭代时(此场景约5分钟),我们的方法也能很好地捕捉到火车。在30000次迭代时(约35分钟),背景伪影显著减少。对于其他场景(下图),差异几乎难以察觉;7000次迭代(约8分钟)时已经具有很高的质量。
训练时间因数据集而异,我们分别报告它们。请注意,图像分辨率也因数据集而异。在项目网站上,我们提供了我们用于计算所有方法(我们的和先前工作)在所有场景上的统计数据的测试视图的所有渲染。请注意,我们为所有渲染保留了原生输入分辨率。
表格显示,我们完全收敛的模型达到了与SOTA Mip-NeRF360方法相当,有时甚至略好的质量;请注意,在相同的硬件上,他们的平均训练时间为48小时²,而我们为35-45分钟,他们的渲染时间为10秒/帧。我们在5-10分钟的训练后达到了与InstantNGP和Plenoxels相当的质量,但额外的训练时间使我们能够达到SOTA质量,这对其他快速方法来说并非如此。对于Tanks & Temples,我们在类似的训练时间(我们的情况下约7分钟)内达到了与基本InstantNGP相似的质量。
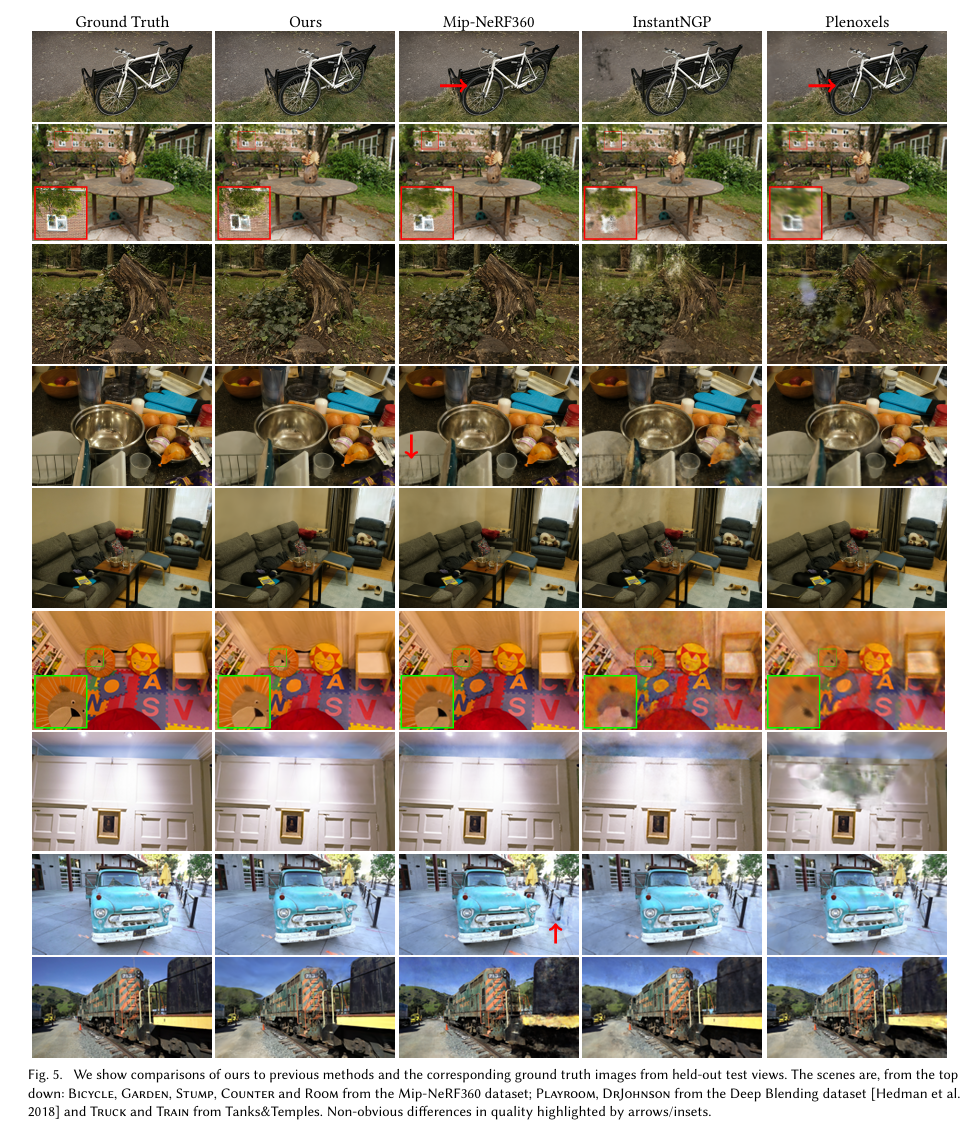
图5. 我们展示了我们的方法与之前方法的比较,以及来自保留测试视图的相应真实图像。场景从上到下依次是:来自Mip - NeRF360数据集的Bicycle、Garden、Stump、Counter和Room;来自Deep Blending数据集[Hedman等人,2018年]的PLAYROOM、DRJOHNSON;以及来自Tanks&Temples的TRUCK和TRAIN。箭头/插图突出显示了质量上不明显的差异。
我们还在图5中展示了我们的方法与选定进行比较的先前渲染方法对于留出的测试视图的视觉结果比较;我们方法的结果是30K次迭代训练的。我们看到,在某些情况下,即使是Mip-NeRF360也有我们的方法避免的残留伪影(例如,植被中的模糊 - 在Bicycle,Stump中 - 或Room的墙壁上)。在补充视频和网页中,我们提供了远距离路径的比较。我们的方法倾向于即使从远处也能保留覆盖良好区域的视觉细节,这并不总是先前方法的情况。
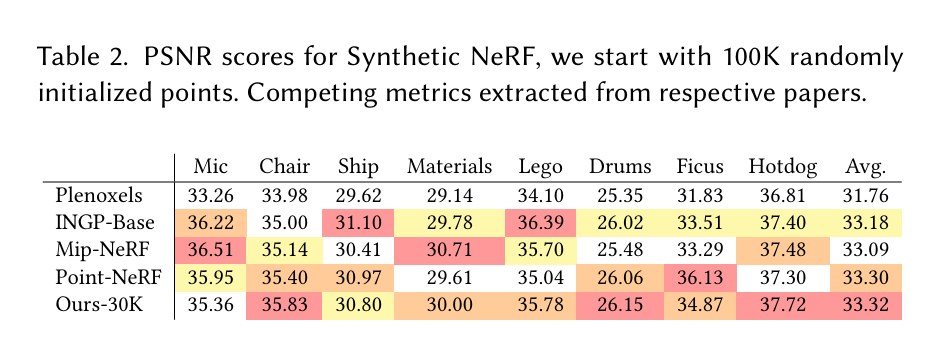
表 2. 合成神经辐射场(Synthetic NeRF)的峰值信噪比(PSNR)分数,我们从 10 万个随机初始化的点开始。竞争指标从相应论文中提取。
合成有界场景。除了真实场景外,我们还在合成Blender数据集[Mildenhall et al. 2020]上评估了我们的方法。这些场景提供了详尽的视图集,大小有限,并提供精确的相机参数。在这种情况下,我们甚至可以通过随机初始化实现最先进的结果:我们从100K个均匀随机分布在包围场景边界的体积内的高斯开始训练。我们的方法迅速自动将它们修剪到约6-10K个有意义的高斯。30K次迭代后训练模型的最终大小达到每个场景约200-500K个高斯。我们在表2中报告并比较了我们实现的PSNR分数与先前方法的比较,使用白色背景以保持兼容性。示例可以在图10(左起第二张图像)和补充材料中看到。训练的合成场景以180-300 FPS渲染。

图10. 我们在禁用和启用高斯各向异性的情况下训练场景。使用各向异性的体素喷溅能够对精细结构进行建模,并且对视觉质量有显著影响。请注意,为了便于说明,在两种配置中我们都限制Ficus使用不超过5000个高斯。
紧凑性。与先前的显式场景表示相比,我们优化中使用的各向异性高斯能够用更少的参数建模复杂形状。我们通过将我们的方法与[Zhang et al. 2022]获得的高度紧凑的基于点的模型进行评估来展示这一点。我们从他们的初始点云开始,该点云是通过前景掩码的空间雕刻获得的,并进行优化,直到我们达到他们报告的PSNR分数。这通常在2-4分钟内发生。我们使用约四分之一的点数超过了他们报告的指标,导致平均模型大小为3.8 MB,而他们为9 MB。我们注意到,对于这个实验,我们只使用了两度球谐函数,类似于他们的。
²我们在4-GPU A100节点上训练Mip-NeRF360 12小时,相当于单GPU 48小时。请注意,A100比A6000 GPU更快。
7.3 消融实验

图3. 我们通过将优化后的三维高斯缩小60%(最右侧)来进行可视化。这清楚地展示了三维高斯的各向异性形状,在优化后紧凑地表示了复杂的几何结构。左侧是实际渲染的图像。
我们隔离了我们所做的不同贡献和算法选择,并构建了一系列实验来测量它们的效果。具体来说,我们测试了我们算法的以下方面:从SfM初始化、我们的密集化策略、各向异性协方差、我们允许无限数量的散射点具有梯度以及使用球谐函数。每种选择的定量效果总结在表3中。
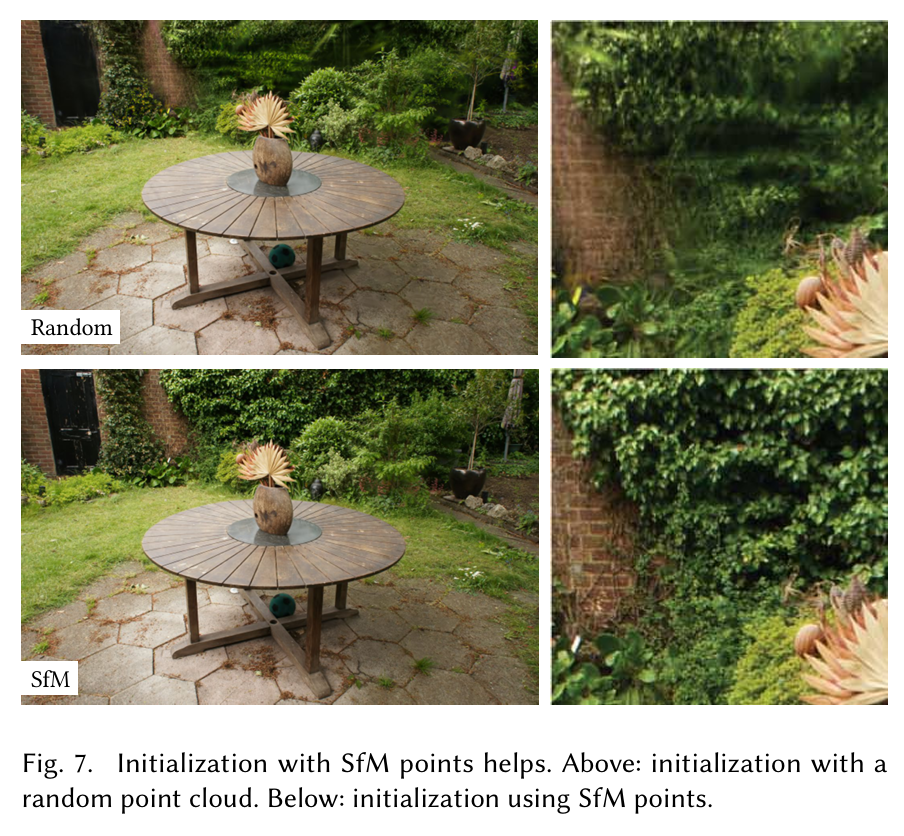

图7. 用运动结构(SfM)点进行初始化很有帮助。上图:用随机点云进行初始化。下图:使用SfM点进行初始化。
从SfM初始化。我们还评估了从SfM点云初始化3D高斯的重要性。对于这个消融实验,我们均匀采样一个立方体,其大小等于输入相机边界框范围的三倍。我们观察到,即使没有SfM点,我们的方法也表现相对良好,避免了完全失败。相反,它主要在背景中退化,见图7。此外,在训练视图未能很好覆盖的区域,随机初始化方法似乎有更多无法通过优化移除的浮动物。另一方面,合成NeRF数据集没有这种行为,因为它没有背景,并且受到输入相机的良好约束(见上文讨论)。
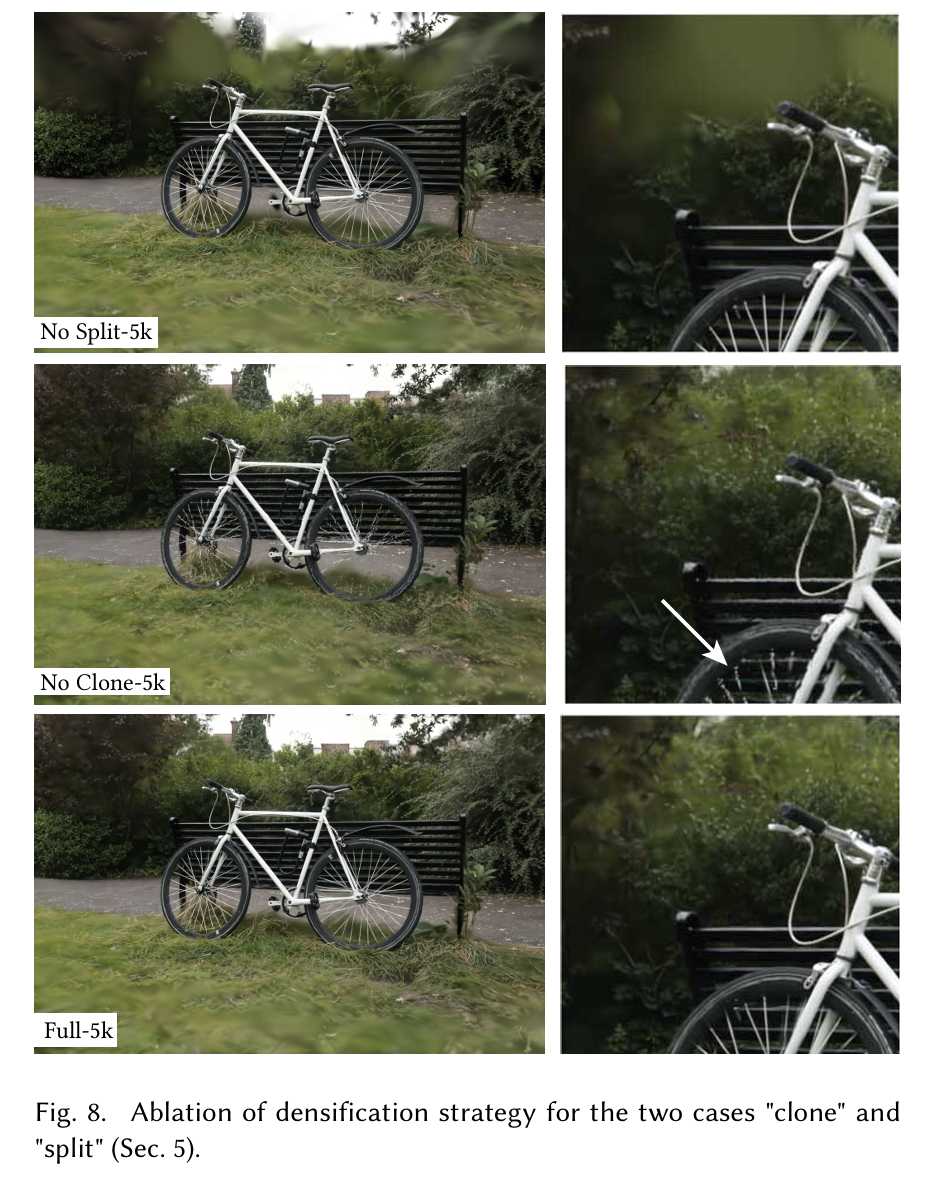

图8. 针对“复制”和“分割”两种情况(第5节)的密度化策略消融实验。
密集化。接下来,我们评估我们的两种密集化方法,更具体地说是第5节中描述的克隆和分裂策略。我们分别禁用每种方法,并使用其余方法保持不变进行优化。结果表明,分裂大高斯对于允许良好重建背景非常重要,如图8所示,而克隆小高斯而不是分裂它们允许更好更快的收敛,特别是当场景中出现细薄结构时。
具有梯度的散射点的无限深度复杂性。我们评估是否在N个最前面的点之后跳过梯度计算会在不牺牲质量的情况下给我们带来速度,如Pulsar[Lassner and Zollhofer 2021]所建议的。在这个测试中,我们选择N=10,这是Pulsar默认值的两倍,但由于梯度计算中的严重近似,导致优化不稳定。对于Truck场景,PSNR质量下降了11dB(见表3,Limited-BW),Garden的视觉结果如图9所示。

图9. 如果我们限制接收梯度的点的数量,对视觉质量的影响很大。左侧:限制10个高斯接收梯度。右侧:我们的完整方法。
各向异性协方差。我们方法中一个重要的算法选择是优化3D高斯的完整协方差矩阵。为了展示这种选择的效果,我们进行了一个消融实验,通过优化控制3D高斯在所有三个轴上半径的单个标量值来移除各向异性。这种优化的结果在图10中直观呈现。我们观察到,各向异性显著提高了3D高斯与表面对齐的能力,这反过来允许在保持相同点数的同时实现更高的渲染质量。

图10. 我们在禁用和启用高斯各向异性的情况下训练场景。使用各向异性的体素喷溅能够对精细结构进行建模,并且对视觉质量有显著影响。请注意,为了便于说明,在两种配置中我们都限制Ficus使用不超过5000个高斯。
球谐函数。最后,球谐函数的使用提高了我们的整体PSNR分数,因为它们补偿了视角依赖效果(表3)。
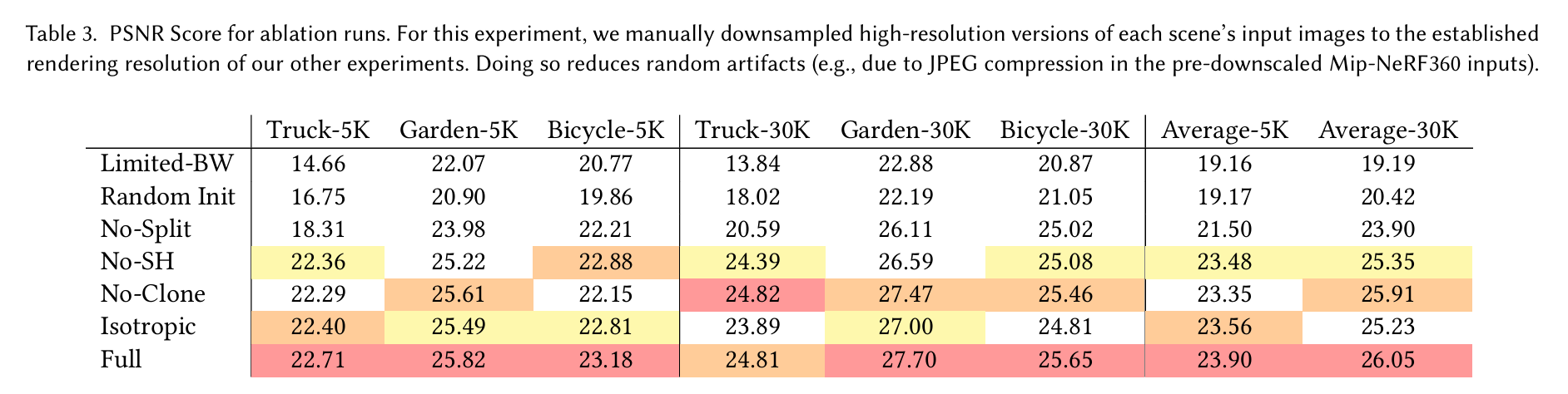
表3. 消融实验的峰值信噪比(PSNR)分数。在这个实验中,我们手动将每个场景的高分辨率输入图像下采样到我们其他实验中设定的渲染分辨率。这样做可以减少随机伪影(例如,由于预先下采样的Mip - NeRF360输入中的JPEG压缩导致的伪影)。
7.4 局限性

图11. 失败伪影的比较:Mip - NeRF360存在“漂浮物”和颗粒状外观(左侧,前景),而我们的方法生成的是粗糙的、各向异性的高斯,导致视觉细节较少(右侧,背景)。TRAIN场景。
我们的方法并非没有局限性。在场景未被很好观察的区域,我们有伪影;在这些区域,其他方法也面临困难(例如,图11中的Mip-NeRF360)。尽管各向异性高斯如上所述有许多优势,但我们的方法可能会创建细长的伪影或”斑点状”高斯(见图12);同样,先前的方法在这些情况下也面临困难。

图12. 在与训练期间所见视图几乎没有重叠的视图中,我们的方法可能会产生伪影(右侧)。同样,在这些情况下Mip - NeRF360也存在伪影(左侧)。DRJOHNSON场景。
当我们的优化创建大型高斯时,我们偶尔也会有弹出伪影;这往往发生在具有视角依赖外观的区域。这些弹出伪影的一个原因是光栅化器中通过保护带对高斯的简单拒绝。更有原则的剔除方法将减轻这些伪影。另一个因素是我们简单的可见性算法,这可能导致高斯突然切换深度/混合顺序。这可以通过抗锯齿来解决,我们将其作为未来的工作。此外,我们目前不对我们的优化应用任何正则化;这样做将有助于解决未见区域和弹出伪影问题。
虽然我们在完整评估中使用了相同的超参数,但早期实验表明,在非常大的场景(例如,城市数据集)中,减少位置学习率可能是收敛所必需的。尽管与先前基于点的方法相比,我们非常紧凑,但我们的内存消耗明显高于基于NeRF的解决方案。在训练大型场景期间,我们未优化的原型的峰值GPU内存消耗可能超过20 GB。然而,通过对优化逻辑进行仔细的低级实现(类似于InstantNGP),这一数字可以显著减少。渲染训练好的场景需要足够的GPU内存来存储完整模型(大型场景为数百兆字节)以及光栅化器额外的30-500 MB,取决于场景大小和图像分辨率。我们注意到,有许多机会进一步减少我们方法的内存消耗。点云压缩技术是一个研究充分的领域[De Queiroz and Chou 2016];看看这些方法如何适应我们的表示将会很有趣。
8 讨论和结论
我们提出了第一个真正允许实时、高质量辐射场渲染的方法,适用于各种场景和捕获风格,同时需要的训练时间与最快的先前方法相当。
我们选择的3D高斯基元保留了体积渲染的优化特性,同时直接允许快速基于散射的光栅化。我们的工作表明——与广泛接受的观点相反——连续表示并非严格必要,以允许快速和高质量的辐射场训练。
我们的训练时间大部分(约80%)花在Python代码上,因为我们在PyTorch中构建了我们的解决方案,以便其他人可以轻松使用我们的方法。只有光栅化例程作为优化的CUDA内核实现。我们预计,将剩余的优化完全移植到CUDA,例如在InstantNGP[Müller et al. 2022]中所做的那样,可以为性能至关重要的应用程序实现显著的进一步加速。
我们还展示了基于实时渲染原则的重要性,利用GPU的强大功能和软件光栅化管线架构的速度。这些设计选择是训练和实时渲染性能的关键,与先前的体积光线行进相比提供了性能上的竞争优势。
看看我们的高斯是否可以用于执行捕获场景的网格重建将会很有趣。除了考虑到网格的广泛使用的实际意义外,这将使我们能够更好地理解我们的方法在体积和表面表示连续体中的确切位置。
总之,我们提出了第一个辐射场实时渲染解决方案,其渲染质量与最佳昂贵的先前方法相匹配,训练时间与现有最快解决方案相当。
致谢
本研究由ERC高级资助FUNGRAPH No 788065 http://fungraph.inria.fr资助。作者感谢Adobe的慷慨捐赠,来自蔚蓝海岸大学的OPAL基础设施以及来自GENCI-IDRIS的HPC资源(授权2022-AD011013409)。作者感谢匿名审稿人的宝贵反馈,P. Hedman和A. Tewari校对早期草稿,以及T. Müller、A. Yu和S. Fridovich-Keil帮助进行比较。
A 梯度计算细节
回顾一下,$\Sigma/\Sigma’$是高斯模型在世界/视图空间的协方差矩阵,$q$是旋转量,$s$是缩放因子,$W$是视图变换,$J$是投影变换的仿射近似的雅可比矩阵。我们可以应用链式法则来求关于缩放和旋转的导数:
\[\frac{d\Sigma'}{ds} = \frac{d\Sigma'}{d\Sigma} \frac{d\Sigma}{ds} \tag{8}\]以及
\[\frac{d\Sigma'}{dq} = \frac{d\Sigma'}{d\Sigma} \frac{d\Sigma}{dq} \tag{9}\]使用$U = JW$ 并且 $\Sigma’$ 是 $U\Sigma U^{T}$ 的(对称)左上角 $2\times2$ 矩阵来简化公式(5),用下标表示矩阵元素,我们可以得到偏导数 \(\frac{\partial\Sigma'}{\partial\Sigma_{ij}} = \begin{pmatrix} U_{1,i}U_{1,j} & U_{1,i}U_{2,j} \\ U_{1,j}U_{2,i} & U_{2,i}U_{2,j} \end{pmatrix}\)
接下来,我们求导数 $\frac{d\Sigma}{ds}$ 和 $\frac{d\Sigma}{dq}$。由于 $\Sigma = RSS^{T}R^{T}$,我们可以计算 $M = RS$ 并将 $\Sigma$ 改写为 $\Sigma = MM^{T}$。因此,我们可以写出 $\frac{d\Sigma}{ds} = \frac{d\Sigma}{dM} \frac{dM}{ds}$ 以及 $\frac{d\Sigma}{dq} = \frac{d\Sigma}{dM} \frac{dM}{dq}$。由于协方差矩阵 $\Sigma$(及其梯度)是对称的,共享的第一部分可通过 $\frac{d\Sigma}{dM} = 2M^{T}$ 简洁地得到。对于缩放,我们进一步有
\[\frac{\partial M_{i,j}}{\partial s_{k}} = \begin{cases} R_{i,k} & \text{如果 } j = k \\ 0 & \text{否则} \end{cases}\]为了推导旋转的梯度,我们回顾从实部为 $q_r$ 、虚部为 $q_i, q_j, q_k$ 的单位四元数 $q$ 到旋转矩阵 $R$ 的转换:
\[R(q) = 2\begin{pmatrix} \frac{1}{2} - (q_{j}^{2} + q_{k}^{2}) & (q_{i}q_{j} - q_{r}q_{k}) & (q_{i}q_{k} + q_{r}q_{j}) \\ (q_{i}q_{j} + q_{r}q_{k}) & \frac{1}{2} - (q_{i}^{2} + q_{k}^{2}) & (q_{j}q_{k} - q_{r}q_{i}) \\ (q_{i}q_{k} - q_{r}q_{j}) & (q_{j}q_{k} + q_{r}q_{i}) & \frac{1}{2} - (q_{i}^{2} + q_{j}^{2}) \end{pmatrix} \tag{10}\]因此,我们得到关于 $q$ 分量的如下梯度:
\[\frac{\partial M}{\partial q_r} = 2\begin{pmatrix} 0 & -s_yq_k & s_zq_j \\ s_xq_k & 0 & -s_zq_i \\ -s_xq_j & s_yq_i & 0 \end{pmatrix}, \quad \frac{\partial M}{\partial q_i} = 2\begin{pmatrix} 0 & s_yq_j & s_zq_k \\ s_xq_j & -2s_yq_i & -s_zq_r \\ s_xq_k & s_yq_r & -2s_zq_i \end{pmatrix}\] \[\frac{\partial M}{\partial q_j} = 2\begin{pmatrix} -2s_xq_j & s_yq_i & s_zq_r \\ s_xq_i & 0 & s_zq_k \\ -s_xq_r & s_yq_k & -2s_zq_j \end{pmatrix}, \quad \frac{\partial M}{\partial q_k} = 2\begin{pmatrix} -2s_xq_k & -s_yq_r & s_zq_i \\ s_xq_r & -2s_yq_k & s_zq_j \\ s_xq_i & s_yq_j & 0 \end{pmatrix} \tag{11}\]推导四元数归一化的梯度很直接。
B 优化和致密化算法

我们的优化和致密化算法总结在算法1中。
C 光栅化器细节
排序
我们的设计基于小“喷绘”(splats)负载较高的假设,为了对此进行优化,在每帧开始时使用基数排序对喷绘进行一次排序。我们将屏幕分割成16×16像素的小块(或称为“箱”)。对于每个喷绘,只要它与某个16×16小块重叠,我们就在该小块中实例化它,从而为每个小块创建一个喷绘列表。这会使要处理的高斯模型数量适度增加,但通过更简单的控制流和优化后的GPU基数排序的高并行性[Merrill和Grimshaw 2010]可以抵消这一点。我们为每个喷绘实例分配一个最多64位的键,其中低32位对其投影深度进行编码,高32位对重叠小块的索引进行编码。索引的确切大小取决于当前分辨率下能容纳多少个小块。因此,通过一次基数排序就能直接并行解决所有喷绘的深度排序问题。
排序后,我们可以通过识别已排序列表中具有相同小块ID的范围的起始和结束位置,高效地生成每个小块的高斯模型处理列表。这是并行完成的,为每个64位数组元素启动一个线程,将其高32位与相邻的两个元素进行比较。与[Lassner和Zollhofer 2021]相比,我们的光栅化完全消除了顺序的基元处理步骤,并且生成了更紧凑的每个小块的列表,以便在前向传播中遍历。算法2展示了我们光栅化方法的高层概述。
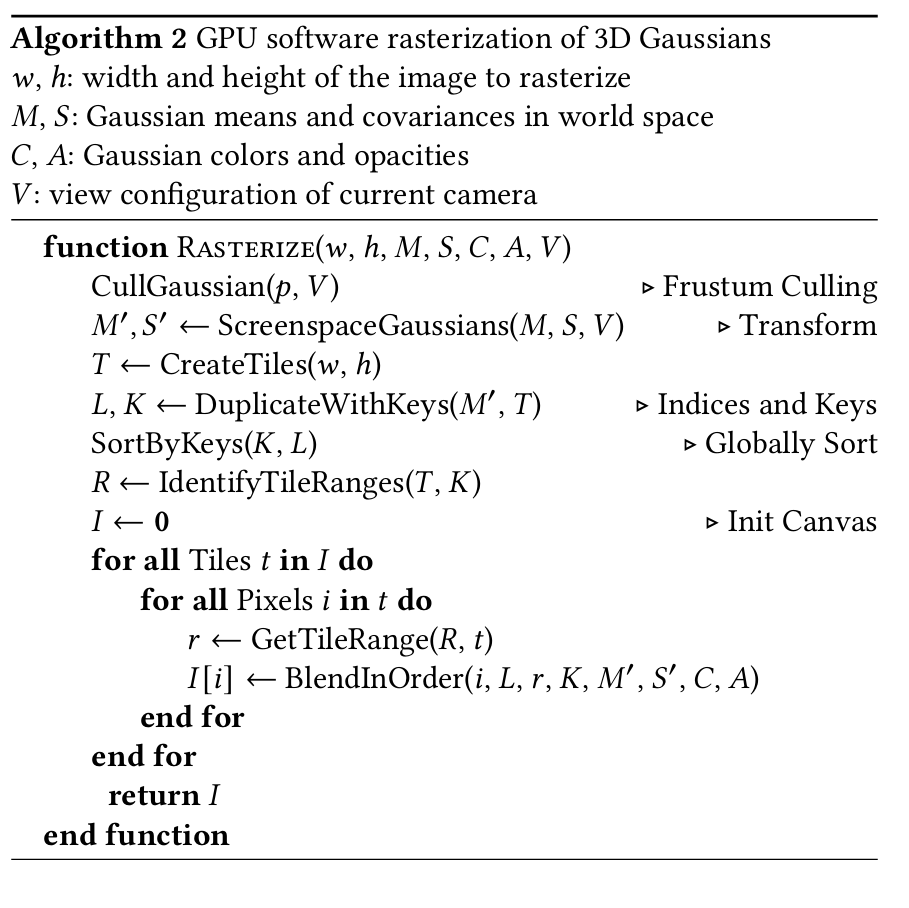
数值稳定性
在反向传播过程中,我们通过将前向传播中累积的不透明度依次除以每个高斯模型的$\alpha$,来重建梯度计算所需的中间不透明度值。如果简单实现,这个过程容易出现数值不稳定的情况(例如,除以0)。为了解决这个问题,在正向和反向传播中,我们会跳过$\alpha < \epsilon$(我们选择$\epsilon$为$\frac{1}{255}$)的混合更新,并且将$\alpha$限制在不超过0.99。最后,在一个高斯模型被纳入正向光栅化过程之前,我们会计算纳入它后的累积不透明度,并在累积不透明度超过0.9999之前停止从前到后的混合。
D 每个场景的误差指标
表4 - 9列出了我们针对所有考虑的技术和真实场景进行评估时收集的各种误差指标。我们列出了从Mip - NeRF360复制的数据,以及我们用于生成论文中图像的运行数据;在整个Mip - NeRF360数据集上,这些数据的平均值为:峰值信噪比(PSNR)27.58,结构相似性指数(SSIM)0.790,以及学习感知图像块相似度(LPIPS)0.240 。
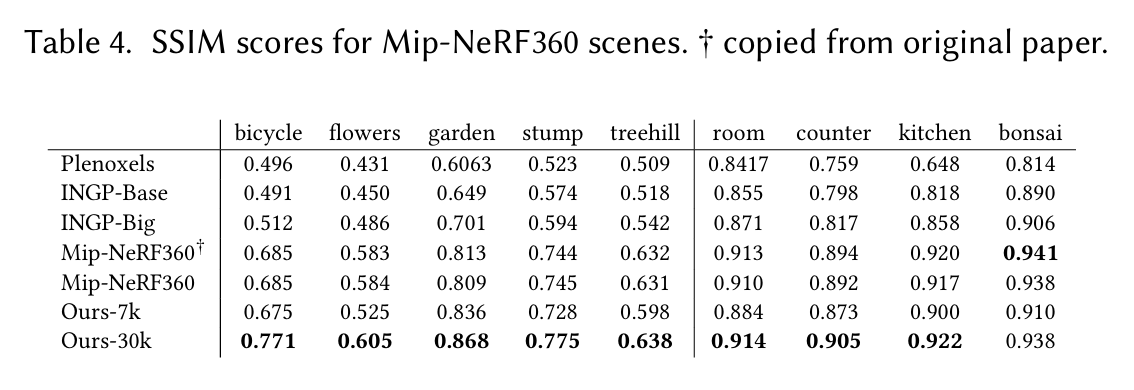
表4. Mip - NeRF360场景的结构相似性指数(SSIM)分数。† 从原文复制。
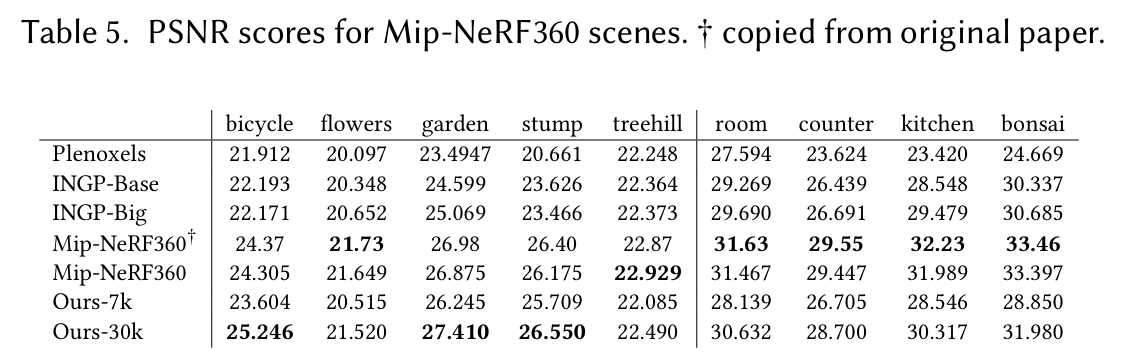
表5. Mip - NeRF360场景的峰值信噪比(PSNR)分数。† 从原文复制。
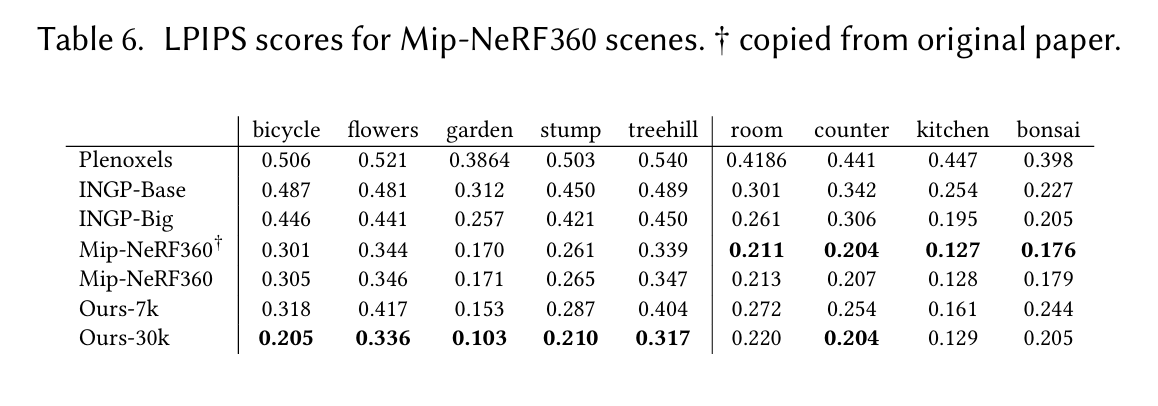
表6. Mip - NeRF360场景的感知损失相似性指数(LPIPS)分数。† 从原文复制。
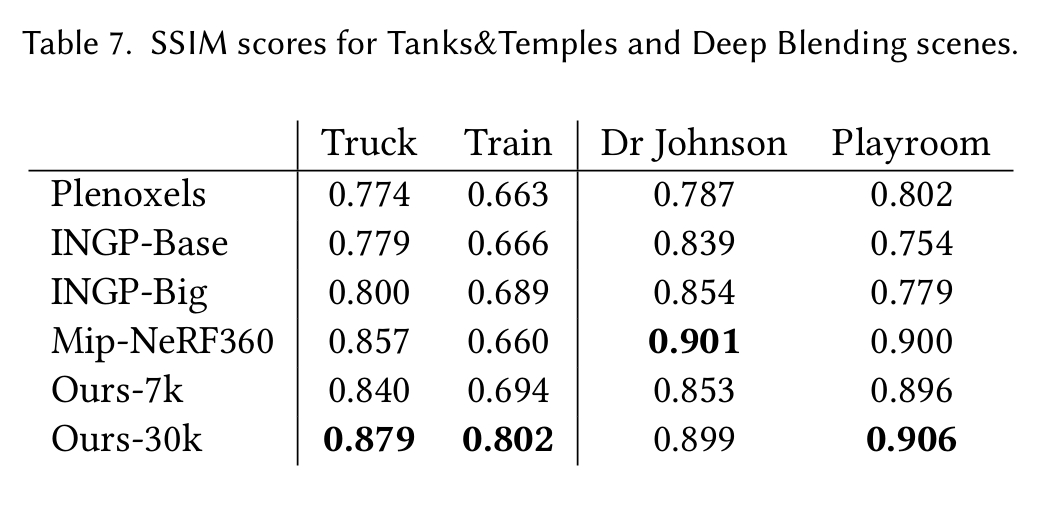
表7. Tanks&Temples和Deep Blending场景的结构相似性指数(SSIM)分数。
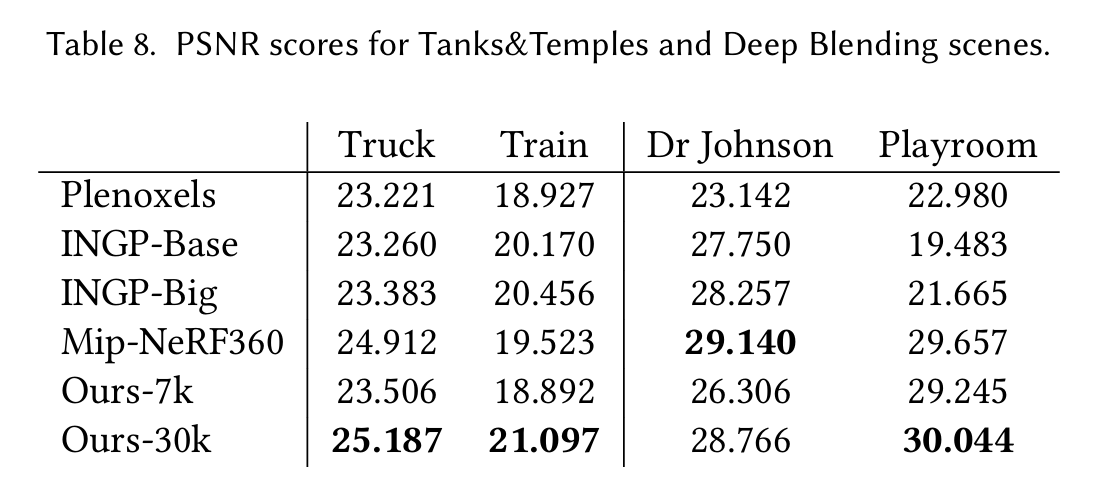
表8. Tanks&Temples和Deep Blending场景的峰值信噪比(PSNR)分数。
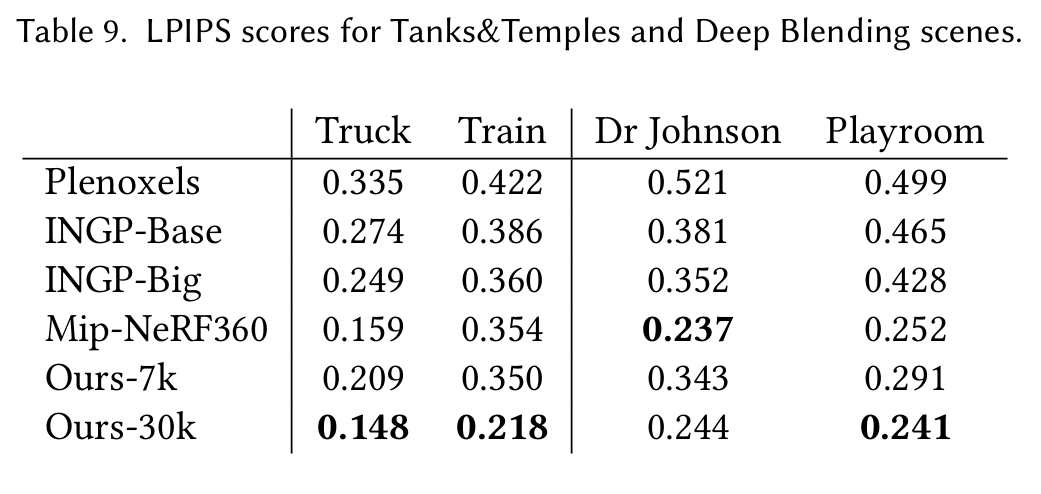
表9. Tanks&Temples和Deep Blending场景的感知损失相似性指数(LPIPS)分数。
评论